The purpose of layout is to arrange the various components within itself according to a particular scheme and the LinearLayout is the simplest of layout which is proposed by default when you create an Android project.
- Create a new Android project
- Edit the file res/layout/main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:gravity="top|left" android:background="@color/yellow" android:text="@string/label1"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="2" android:layout_gravity="center" android:gravity="center" android:background="@color/green" android:layout_margin="50px" android:text="@string/label2"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="3" android:gravity="bottom|right" android:padding="50px" android:background="@color/fuchsia" android:text="@string/label3"/> </LinearLayout> - Edit the file res/values/strings.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">Hello World, LinearLayoutTutorialActivity!</string> <string name="app_name">LinearLayoutTutorial</string> <string name="label1">one</string> <string name="label2">two</string> <string name="label3">three</string> </resources> - Create the file res/values/colors.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <color name="yellow">#FFFF00</color> <color name="fuchsia">#FF00FF</color> <color name="green">#008000</color> </resources>
- Verify that the main class has the method:
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); }
The end result seen by the emulator is as follows:
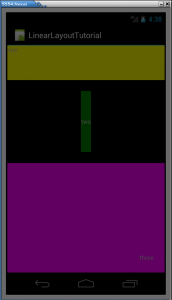
The Linearlayout arrange the components in or portrait or landscape orientation, you can verify this aspect replacing android: orientation = “vertical” with android: orientation = “vertical”in the file main.xml.
The dimensions of the components are mainly determined by android:layout_width and layout_height whose values can be set to:
- fill_parent: the component fills all available space (deprecated)
- match_parent: the component fills all available space
- wrap_content: the component gets enough space to show their contents
- [a number]: specify an exact number in px (pixels), dp (density-independent pixels), sp (scaled pixels based on preferred font size), in (inches), mm (millimeters)
The dimensions of the components can be increased or decreased value to android:layout_weight, and the components for which a value is specified for android:layout_weight have relative size proportionate to that value.
android:layout_gravity e android:gravity set similar characteristics but on different objects:
- android:layout_gravity: sets the positioning of the component relative to the layout
- android:gravity: sets the positioning of the body of the component relative to the same component.
You can specify multiple values separated by the character “|”, for example: android:gravity=”bottom|center”.
android:padding sets the distance between the body of the component and the edge of the component.
android:layout_margin sets the distance between the component from the edge of the layout or other elements.
android:padding e android:layout_margin can also be set for layout.

Leave a Reply